Below we have discussed the structure of class 1 and class 2 MUC.
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) is called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex in humans and the H-2 complex in mice. Almost all human cells contain HLA molecules on their plasma membranes, only RBC cells do not have MHC. HLA molecules can be divided into three classes;
Class 1 molecules are found on all type of nucleated body cells.
Class 2 molecules appear only on cells that can process non self materials and present antigens to other cells (i.e., macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells).
Class 3 molecules include various selected proteins that have immune function.
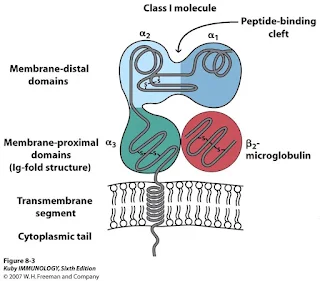
Class 1 MHC
- Class 1 MHC molecules consist of a complex of two protein chains, one with a mass of 45,000 Daltons (Da), alpha chain, beta 2- microglobulin.
- The alpha chain can be divided into three functional domains, designated alpha 1, alpha 2, alpha 3. Only non- nucleated cells ( red blood cells) lack class 1 MHC molecules.
- Beta 2- Microglobulin:- It is associated with a non-covalently linked, which helps in stabilizing the structure but is not encoded by the MHC gene complex .
- The alpha 1 and alpha 2 domains form the peptide binding groove, where antigens are presented. This groove accommodates peptides that are typically 8-10 amino acids long.
Function
- MHC class I molecules present peptides derived from intracellular proteins to cytotoxic T cells ( CD8+ cytotoxic T cells).
- This pathway is crucial for the detection and elimination of infected or malignant cells.
- If the CD8+ T cells recognize the presented peptide as foreign, they initiate a response to kill the infected or abnormal cell.
Class 2 MHC
- Both the alpha and beta chains contribute to the formation of the peptide-binding groove.
- The alpha 1 and beta 1 domains form the peptide binding groove, which can bind longer peptides, typically 13-25 amino acids.
- Both α and β chains span the membrane and anchor the molecule to the cell surface.
- Cytoplasmic tails: Extend into the cell and help in signaling and transport.
- Found only on antigen-presenting cells (APCs): dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells.
Function
- MHC class 2 molecules present peptides from extracellular sources (eg., bacterial proteins, toxins) to helper T cells ( CD4+ cytotoxic T cells).
- This is critical for initiating immune responses such as antibody production and activating other immune cells.
- MHC class 2 molecules are primarily expressed on antigen - presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells.



Post a Comment