Corona virus is an infectious disease cause by the SARS-CoV-2 virus( severe acute respiratory syndrome). The disease was spread world wide resulting in COVID-19 pandemic. COVID-19 transmission was originated from China and was slowly spread to all the countries. COVID-19 has head Protein health, social, economic impacts globally.
Morphology of COVID-19
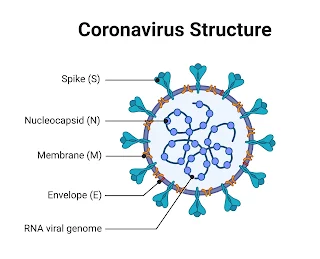
- Shape – spherical to pleomorphic.
- Size – Approx 60-140 nm in diameter.
- Envelope – a lipid bilayer derived from the host cell membrane surrounds the virus.
- Spike (s) protein – forms crown- like spikes (~20nm long) on the viral surface.
- Membrane ( M) protein – determine the shape, most abundant protein in the vision.
- Nucleocapsid (N) protein – encapsulates the single - stranded, positive - sense RNA genome.
- Genome – ~30kb in length, encodes non- structural proteins like RNA- dependent RNA polymerase ( RdRp), essential for viral replication.
- Surface features – Glycoproteins protrude from envelope, forming spikes " crown"( hence name corona virus).
Pathogenesis of corona virus

- Viral Entry – SARS–CoV–2 enters the body through the respiratory tracts, binding to ACE2 receptors and host cells, primarily in the lungs and other organs.
- Viral Replication – The virus replicates inside host cells, producing new viral particles and spreading to nearby cells.
- Immune Response – The body's immune responds, leading to inflammation. In some cases, an overactive immune response ( cytokine storm) causes tissue damage.
- Tissue damage – Viral replication and inflammation damage the lungs ( causing pneumonia, ARDS) and can affect other organs like the heart kidneys and gastrointestinal system.
- Clinical Manifestation – symptoms range from mild ( fever, cough) to severe ( difficulty breathing, organ failure) some people develope " long COVID" with persistent symptoms after recovery.
Clinical systems of Corona virus.

- Fever – A common symptom indicating infection.
- Cough – usually dry and persistent.
- Difficulty Breathing – can range from mild to severe.
- Fatigue – feeling tired or weak.
- Loss of taste or smell – A unique symptom for many patients.
- Muscle or body achese – general discomfort and pain.
- Sore throat – Irritation in the throat.
- Headache – common among infected individuals.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms – such a diarrhea or nausea in some cases.
Lab diagnosis of corona virus
1. Specimen collection:-
Nasopharyngeal swab, oropharyngeal swab, sputum , saliva, bronchoalveolar lavage ( fluid in severe cases).
2. Rapid Antigen Test:-
- Detects viral proteins ( antigens) in respiratory sample.
- It glued quick result in is to 30 minutes.
- It has lower sensitivity compare to RT-PCR .
- Detects antibodies like IgM, IgG, IgA produced in response to the virus.
- Specimen blood ( serum or plasma).
5. Viral culture:-
Mainly the virus is grown in the host, model animals in a controlled laboratory setting.
6. Chest imaging :- CT scan or X- ray.
Prevention

- Vaccination :- Covishield & Covaxin.
- Hygeine practices :- wash hand frequently with soap and water.
- Masking :-were mask in crowed or properly ventilated area.
- Social distance :- minimum to 2 meter physical distance was maintained from other good ventilation.
- Avoiding close content with sick people.
Treatment
Antiviral medication, rest proper hydration, proper diet.



Post a Comment